Brief Introduction
e-invoicing has become a popular trend in indirect taxation in the past few years in the world. The major and important reason to implement GST is to curb tax evasion from the country and to have transparent and real or near real-time reporting to the government for every transaction made by businesses. It gives a clear image of the businesses’ taxation compliance or tax obligations to the government. Many countries have already implemented e-invoicing systems. Now government of India has also introduced an e-invoicing system in the country.
What is e-invoicing?
Electronic invoicing or e-invoices is the reporting and authentication of the B2B (Business to Business) invoice generated by a registered person on its existing billing system on IRP (Invoice Registration Portal).
When invoices are authenticated by the IRP (Invoice Registration Portal), a unique IRN (Invoice Registration Number) also known as Hash is generated and invoices are digitally signed and a QR code is added to it, which is then called the generation of an E-invoice.
The first portal launched by NIC is on the direction of the GST council. Many other portals will be issued for the smooth working of the system. Cygnet is one of the IRPs.
- Documents and Supplies covered in e-invoicing
GST Tax Invoices, Debit Notes, and Credit Notes issued for B2B transactions and export transactions are covered in e-invoicing.
How does e-invoicing differ from regular invoicing?
e-invoicing does not mean digital invoicing or invoice creation on a government portal, or a digital copy of an invoice issued through some software or portal. It means authentication of the regular invoice which is already issued by the registered person in its existing Invoice Generation software or system.
When the required details are uploaded and verified on the IRP, a unique IRN of 64 digits and a unique QR code containing the required details of the invoice are generated along with a digital signature attached to the invoice.
When did e-invoicing come into force in India? To whom it is applicable and who is exempted?
In its 37th meeting on 20th September 2019, the GST Council recommended the introduction of electronic Invoices (‘e-Invoice’) in GST in a phased manner based on the annual aggregate turnover (AATO) of the business. The first phase of e-invoicing was made applicable from 1st October 2020.
- Phases in e-invoicing
In the first phase, covering the big industries having business annual aggregate turnover (AATO) exceeding 500 crores were required to generate E-invoices from 1st October 2020.
The Second Phase, covering Medium Enterprise, was introduced on 1st January 2021, for the business whose annual aggregate turnover (AATO) exceeding 100 crores was required to generate an E-invoice.
The Third Phase, covering the small manufacturing and service units, was introduced on 1st April 2021, for the business whose annual aggregate turnover (AATO) exceeding 50 crores was required to generate E-invoice.
In the Fourth Phase, introduced on 1st April 2022, the businesses whose annual aggregate turnover (AATO) exceeded 20 crores were required to generate E- -invoices.
In the Fifth Phase, introduced on 1st October 2022, businesses whose annual aggregate turnover (AATO) exceeded 10 crores were required to generate E- -invoices.
Currently, the Sixth Phase is made applicable from 1st August 2023, covering small and micro manufacturing and service units, to businesses whose annual aggregate turnover (AATO) exceeds 5 crores are required to generate E-invoices.
Taxpayers Exempted from e-invoicing
- Businesses having AATO below 5 crores.
- SEZ units
- An insurer, banking company, or financial Institution including NBFCs.
- Goods Transport Agencies (transportation of goods by road in a good carriage)
- Passenger Transport Service
- A Registered person supplying service by way of admission to the exhibition of cinematographic film in Multiplex services.
- Government departments and local authorities
- Person registered as per Rule 14 of CGST Rules, 2017 (OIDAR)
Mandatory fields of E-invoices

- E-invoice Schema
The GST council provides a standard format known as the E-invoice Schema. Schema is a standard format for E-invoice which has all details like commercial invoices. This Schema format in GST is as per Form GST INV-01.
There are 12 sections (5 mandatory) and six annexures (2 mandatory) comprising 138 fields. The scheme ensures that the E-invoice is machine-readable and interoperable i.e., invoices can be exchanged between different systems and software.
This schema has mandatory as well as optional fields. IRN is generated after the validation of such mandatory fields.
- Major Sections and Annexures of mandatory fields
- Sections:
- Basic details
- Supplier’s information
- Recipient’s information
- Invoice item details
- Document total
- Annexures
- Invoice Item Details
- Document Total Details
How is an E-invoice Generated?
The steps to generate an E-invoices are as under:
- Taxpayers can generate regular invoices in its existing billing system. However, the invoice must contain all mandatory fields required.
- All the invoices generated need to be uploaded to the IRP portal to validate and generate IRN. The following methods can be used for uploading invoices:
- Use of online utility provided in the E-invoice portal to fill in the details online.
- Bulk generation tool provided in E-invoice portal, where a JSON file of invoices can be uploaded.
- Invoice JSON uploads through directly integrating taxpayers’ system through API or GPS (GST Suvidha Provider like Cygnet).
- IRP will generate a unique 64-digit IRN also known as Hash after validation of mandatory fields and add a QR code and digital sign in the output JSON.
- The information of the E-invoice shall be shared with the GST Portal and E-way bill automatically on the generation of IRN.
- Taxpayers shall get an E-mail notification on a generation of E-invoices if an E-mail address is available and forwarded to recipients automatically.
Penalties for Non-compliance
- For non-generation of E-invoice:
- 100% of Tax due Or Rs 10,000 Whichever is Higher
- For incorrect E-invoice generation:
- Rs 25000 per invoice
Advantages of e-invoicing
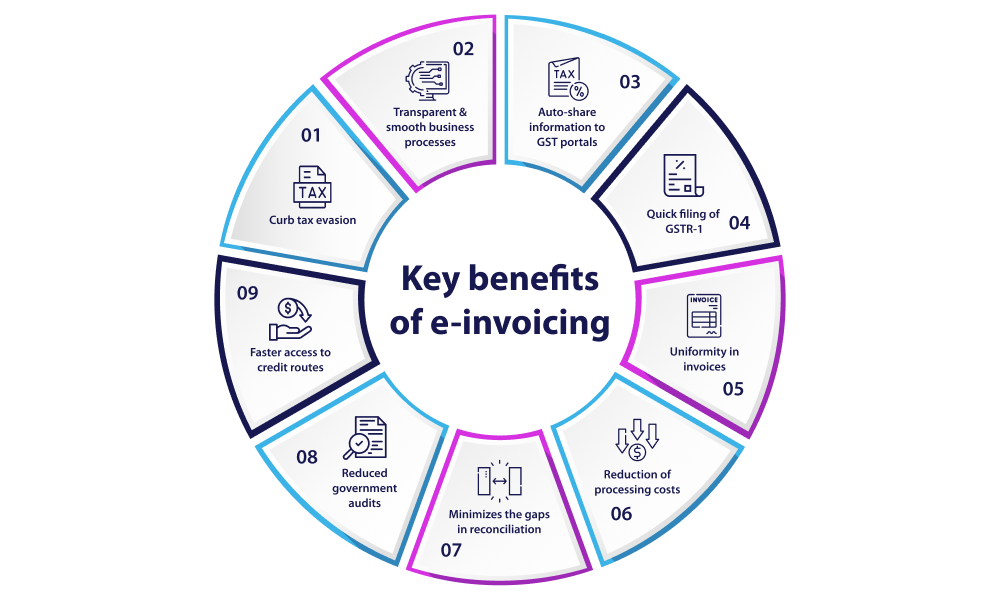
- The primary benefit of e-invoicing is to curb tax evasion.
- e-invoicing provides transparent and smooth business processes or workflow, leading to quicker payment cycles and thereby improving overall business efficiency and cash flow.
- e-invoicing will auto-share information to all the GST portals, say the GST portal and E-way bill Portal which helps in auto-populating GSTR-1 and E-way bills respectively thereby eliminating the errors that occurred due to manual punching of data.
- Once the invoice is uploaded the information will be available to all portals which helps in quick filing of GSTR-1 and generation of the E-way bill.
- E-invoices are generated in standard format due to which there will be uniformity in invoices and important details will be available without any error.
- It helps businesses in the reduction of processing costs.
- Disputes and litigations will be minimized.
- Minimizes the gaps in reconciliation and tax payments and ITC availment shall be more accurate.
- Reduced government audits as the information is already available to government authorities in real-time.
- Faster access to credit routes like invoice discounting and financing.
In Summary
Overall, it’s clear that the introduction of e-invoice has brought a remarkable change in the business process in India, giving transparency and uniformity in maintaining and sharing information. It has also assisted the government in preventing tax evasion and keeping track of all the transactions conducted by businesses. To conclude, e-invoicing may be considered one of the most significant steps for businesses toward moving into this continuously evolving digital era.
Why Choose Cygnet for your e-invoice generation and compliance?
Cygnet is one such IRP that can help businesses and taxpayers upload and generate e-invoices for their transactions. As an IRP Cygnet:
- Automate the upload of invoices to IRP through Cygnet and get IRN responses in bulk.
- Print and download individual and bulk invoices with QR Code and IRP’s Acknowledgement in PDF.
- Cygnet will validate complete invoice data about GST, E-Way Bill, and e-invoicing before IRN Generation.
- Cygnet will sync original invoices with invoices pushed to IRP/GSTN and provide a Reconciliation Report.
- Cygnet will store and provide downloading of original invoices.
- Sends updates to the respective people.
Moreover, it also assists with canceling e-invoices and generating IRNs or QR codes.